In the first article of this series outlining the key players on the IoT connectivity market we looked at distinctive features and theoretical capabilities of the major LPWAN networking solutions. This time we’ll be focusing on how these technologies have been applied in our brave new world, what benefits these pioneer developments reaped, and what challenges surfaced in the course of their rollout and operation.
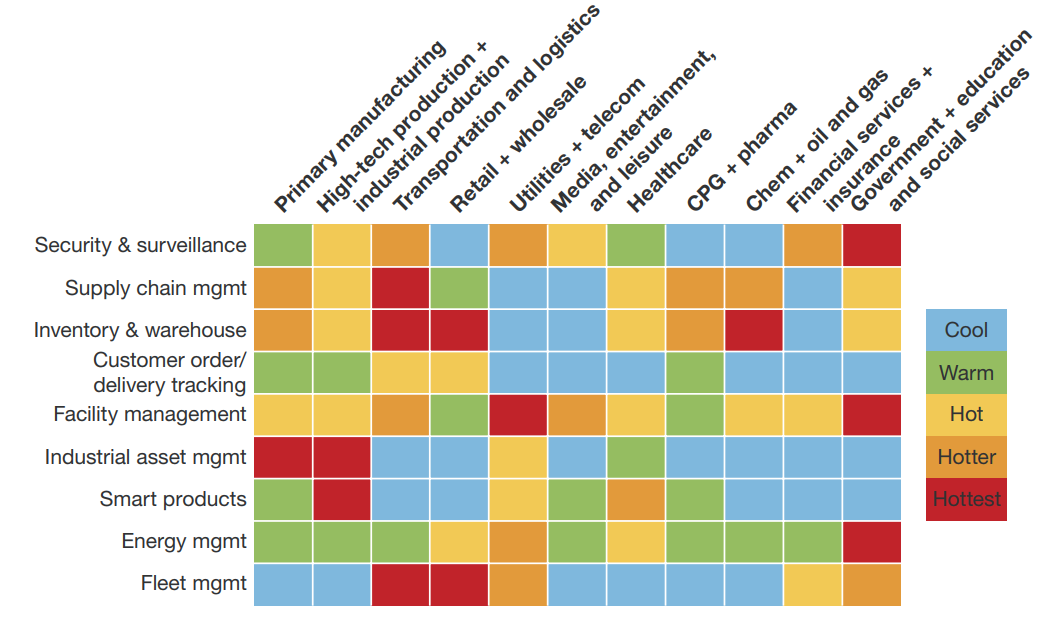
With the wave of ubiquitous connectivity rising and gaining momentum in the lead-up to the giant flush, we start seeing the first sprinkles here and there which are harbingers of the global IoT spread-out. The current disparate attempts are mostly local or dedicated solutions, part of which are trials or pilot launches focused on testing and tweaking the deployed infrastructure. Nevertheless, the early adopters are quite evident even at this initial stage. The heat map below illustrates which industries and which specific functional areas within these industries are taking advantage of the IoT more actively and which ones are reluctant to add the latest connectivity developments to their business toolkits.
In this analysis, we try to sketch the landscape of currently implemented LPWAN networks powered by different IoT connectivity providers, contemplate on the future perspectives and most anticipated advances in the field of IoT connectivity.
Use Cases
Digital Oilfield
Technology: RPMA
Country: Nigeria
Industry: Oil & Gas
Niger Delta is one of the richest oil basins in Africa making Nigeria one of the biggest oil producers on the continent. Shell Nigeria, a leading operator in the area, wanted to optimize its operations, improve performance, as well as ensure a safer working environment for its workers. They ended up creating a connected oilfield based on RPMA technology.
What was done to create a connected oilfield:
- sensors installed on flow-stations, manifolds, wellheads, and in customers’ facilities
- secure bidirectional communication ensured between the oilfield and the office to track pipeline pressure, temperature and flow in real time on the one side, and perform over-the-air device management and battery control on the other side
- reliable battery-powered device operation in a harsh environment guaranteed
- software connectivity and data reporting improved in cooperation with KONČAR (also a device supplier) and Upland Consulting Nigeria
Outcomes:
- enhanced working conditions due to preventive maintenance and better alarm reporting
- reduced downtime and more efficient operations due to real-time equipment monitoring
- extensive production data capturing for advanced analytics and further business development
Connected train
Technology: Sigfox
Country: France
Industry: Supply chain
Danone Waters, a natural, flavored, and vitamin water business of Danone corporation, was seeking to optimize its logistics operations by switching from automotive to railroad transportation. The major concern was the absence of real-time rail fleet tracking, which together with extensive idle periods and inefficient maintenance led to poor performance albeit lower price. To resolve these issues IDEO (a branch of ID Logistics Group) created the first private railway freight hub in Europe using Sigfox network for connectivity.

What was done to create a connected train:
- 1200 wagons equipped with Everysens sensors powered by Sigfox to ensure real-time visibility, preventive maintenance, route and load optimization
- 3-5 years of battery life guaranteed. Since no remote management was needed a one-way communication provided by Sigfox was sufficient and allowed to minimize power consumption
- Everysens software platform set up to enable powerful big data analytics and drive data-based decisions
Outcomes:
- continuous traceability of produce along the way allows to better predict ETA and optimize shipments schedule accordingly
- reduced fleet downtime and consequently higher utilization rate result in higher business value per wagon
- consistent data input allows for better predictive analytics and smarter decisions as the volume grows
Street lighting remote management
Technology: LoRa
Country: Hungary
Industry: Smart cities
This municipal project implemented in a small town in the suburbs of Budapest was initiated by Hungarian government as a pilot attempt to automate and rationalize electricity management with plans to scale it across Hungary if successful. The challenge was to provide reliable long range communication between sensors installed on the lamp posts and management software. The solution was deployed using LoRa technology, LoRaWAN network management server, and the inteliLIGHT CMS application software.
What was done to create a street lighting management system:
- infrastructure deployed within 3 days due to plug-and-play nature of sensors
- bi-directional long range communication established to support up to 20,000 end-devices operating within 15km from the base station
- 1 base station installed on top of the mayor's office building to cover the entire area (approx. 500 lamps)
Outcomes:
- improved and more intelligent lighting management paired with significant savings in power consumption
- streetlight control software enables 24/7 real-time remote control and grid monitoring to track electric parameters at lighting panels level and optimize functional parameters
- understanding of the hurdles to overcome when implementing the solution on a larger scale
Further, we will give a couple more examples in lesser detail.
Smart parking
Technology: NB-IoT
Country: Norway
Industry: Smart cities
Telia company installed over 110 NB-IoT-enabled parking sensors at the municipal parking in Oslo. Using the companion app car drivers can see which spaces are vacant. The sensors are active only when the car arrives at the parking space or vacates it; at all other times the sensors are idle and can operate for years before the battery requires replacement. Since NB-IoT works just fine with the existing 4G base stations, investments in infrastructure are minimal. The next step is to implement remote space booking in the app to make commutes more enjoyable and predictable. An important “side effect” is that the data collected by the app can be used to analyze demand patterns and plan new parking lots and fares more intelligently.
Commercial Trials
Technology: LTE-M
Country: USA
Industry: multiple
AT&T won the race with Verizon by launching the first LTE-M network in November 2016. Their commercial pilot was introduced in San Francisco and was supported by five influential partners: PepsiCo interested in smart vending, Samsung exploring ways to improve customer experience with wearables and consumer devices, Badger Meter implementing smart water metering solutions, CalAmp enabling commercial vehicle and asset tracking, and Capstone Metering aiming to enhance smart cities sensor technologies.
AT&T has ambitious plans to deliver nationwide LTE-M coverage throughout the USA and Mexico by the end of 2017 and invites numerous companies (including Altair, Ericsson, Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Sierra Wireless, u-blox, etc.) to test versatile projects across industries and applications in their network.
***
We were trying to have equal representation of most popular LPWAN technologies across different industries here, but since some technologies are currently being standardized and tested not much information is available on their practical uses.
Now we want to highlight some of the trending themes and deduce what the near future holds for this booming market.
Trends and Forecasts
Agriculture
- smart farm management platforms will store and analyze farm’s history, know the behavior of individual crops strains and the local weather forecast, and will make recommendations to the farmer
- sensors spectroscopically measure the nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium composition of liquid manure as it is being sprayed, allowing real-time adjustments to the spray rate
- integration of aerial and satellite coverage to get both the surface and the synoptic views at once
- LED-illuminated hydroponic indoor (or even underground) farms will be taking advantage of sensors precisely measuring temperature, humidity, and illumination and will give only as much of those as needed leading to rational and analytics-based resource management
- solar-powered robots are being developed to detect the weeds on the fields and eliminate them with a targeted dose of pesticides causing no harm to the plants (pesticides can later be replaced by microwaves, or even a laser to comply with “organic” label requirements)
Healthcare
- a multitude of wearable devices will be streaming the data to caregivers forming huge databases allowing to improve individual treatments as well as the best practices in the field
- smart inventory control systems will make sure the hospital never runs out of critical medicines by scheduling replenishment based on demand forecasts
- preventive maintenance and remote troubleshooting for medical equipment will reduce downtime and human error thus making the machines turn profitable in a shorter term
Smart cities
- lighting will dynamically adapt to the level of daylight and weather conditions, while traffic lights will adapt timing based on the traffic density
- sensors will measure the fullness of waste bins and optimize the routes of waste trucks and frequency of emptying
- next generation wearable devices will measure air quality, temperature, humidity, UV level etc. to create a crowdsourced map of environmental data in real-time and make healthier choices
Transportation
- vehicles featuring augmented driving capabilities will analyze the state of all internal systems as well as the surrounding conditions (surface quality, road boundaries, speed limits, traffic density, ambient light, etc.) to optimize performance and give suggestions on the fly
- driverless cars will go (and already go) even further and turn the driver into another passenger
- huge savings are associated with the use of sensors in aircraft — Boeing gets data from around 1 mln checkpoints to sense issues before the pilot see them on the dashboard
Manufacturing
- tracking the use of the product throughout its lifecycle will help manufacturers better understand what functionality is used more or if any usability issues arise making new product development more grounded and demand more predictable
- predictive and preventive maintenance help save millions by reducing downtime and freeing time for productive actions; monitoring the amount of emission through filtering systems may help avoid fines for exceeding the allowed levels
- sensors will provide real-time visibility into all steps of the production process facilitating detection of bottlenecks or unused capacity; as enough data is accumulated more efficient production lines can be designed and spare resources reallocated to generate profit
Oil & Gas
- tracking the state of the infrastructure remotely and in real-time helps workers stay safe by handling most emergency operations automatically
- monitoring is becoming possible in hard-to-reach places and in harsh conditions helping collect critical data about most loaded and accident-prone areas
- leak detection along the pipelines will increase company revenues while minimizing the environmental impact caused by the industry
Supply chain
- asset tracking and fleet management become the required base level to stay competitive — knowing the utilization rates, driving patterns, and truck capacity used allows a substantial reduction of fixed costs and faster delivery times
- RFID and more advanced NFC tags are switching inventory and warehouse management into the new level — tracking individual items is now possible once it has been manufactured. This gives vast opportunities for replenishment scheduling to balance short stocks and excess items sitting on the shelves
- tons of data collected by different companies at different stages of the supply chain can be shared and combined for more complex analysis of the industry as a whole with insights potentially beneficial for all parties (including the customer).
One doesn’t need to be a prophet to state that IoT invasion is definitely happening. We already have smart beds, smart speakers, and smart cars. But where do we invest our own smartness? Into creating something even smarter or making smarter use of what is already available? Hopefully both.
As you can see currently it’s all about preventing rather than reacting, saving and optimizing rather than wasting, making informed decisions rather than wild guessing. Further advancements should allow detection of interdependencies and interconnections invisible to the human eye due to zillions of data points involved in the analysis. IoT connectivity options should evolve in sync to facilitate deployment of new, more sophisticated projects. 5G creeping into the infrastructure of several countries means new developments in IoT by cellular operators. Proprietary technologies are also keeping up extending their networks, supporting more device types, and earning the support of industry behemoths.