On the way to launch flespi gateway we pay special attention to the questions of possible platform use cases. And the most important task for any use case is to describe the process of consuming new messages from devices. Besides a widespread REST API technology we have introduced Swagger-generated API clients for some popular languages. And if REST API is just a common and multi-platform way for application interaction and Swagger clients provide easy-to-use method wrappers for REST API calls, we are ready for the next step - to provide a library with a computationally efficient model of message consumption and extendable architecture.
flespi receiver
Let me introduce a Python module flespi_receiver. Here are the library basic features:
- python 3.5 project with an asynchronous architecture using python-asyncio;
- REST API calls to flespi platform are made with reduced swagger-generated API that uses python-urllib3;
- open source: all benefits of MIT license allowing to use this library anyhow;
- object-oriented structure: received messages are processed by handlers, each handler is an independent instance of a subclass derived from an abstract base class with a common handler structure

To simplify, let’s consider a basic use case: consume messages from flespi channel and print it to stdout. To do this you need to:
- create an instance of flespi receiver class
- configure it with an authorization token and a target channel ID
- create an instance of stdout handler class and add it to flespi receiver handler list
- start flespi receiver and see received messages in stdout as soon as they appear in a channel
The code of these steps is available in the project’s test location.
Creating a handler
And much more valuable question for dear reader is "What handlers are available for now?". Well, I have to admit that there are only two handler types: printing to stdout (mostly to test architecture) and Wialon retranslator protocol (for our internal use to integrate flespi to Wialon services). But don’t give up, in the next few minutes you will see that implementing new handlers is easier than a piece of cake due to both Python language advantages and flespi_receiver library scalability. And along with creating a new handler we will take a closer look at the library architecture.
We consider the following task: redirect message flow from a flespi channel to Amazon AWS IoT service. According to AWS IoT Python SDK documentation:
- AWS IoT client uses MQTT protocol, security is provided by certificates and private keys;
- an entrance point to the service is called “endpoint” (analogue of flespi channel uri);
- pip package AWSIoTPythonSDK is responsible for work with the service from the client’s side on Python.
Next see the process of implementing AWS IoT client in the library:
1. Add AWSIoTPythonSDK module to project dependencies
A library requiring modules list is placed in the requirements.txt file and will be installed on "make init" command.
2. Create a new class for AWS IoT handler
Create a file flespi_receiver/aws_iot_handler.py. Include module from AWSIoTPythonSDK:
from AWSIoTPythonSDK.MQTTLib import AWSIoTMQTTClient
and import json module as AWS accepts messages in a JSON format:
import json
A new handler class must have a structure defined in an abstract base class handler_class: __init__ constructor and an abstract method _workout_messages with fixed signature (to handle messages from flespi channel) must be defined.
Declare the class as deriving from handler_class:
from .handler_class import handler_class
class aws_iot_handler_class(handler_class):
Handler constructor must verify input configuration parameters and initiate AWS IoT client:
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
/* verify required input parameters */
required_args = ['root_ca_path', 'private_key_path',
'certificate_path', 'endpoint']
for param_name in required_args:
if param_name not in kwargs:
print('Amazon AWS IoT handler: missing parameter ' + param_name)
raise ValueError
/* init Amazon AWS IoT client */
self.aws_iot_mqtt_client = AWSIoTMQTTClient("flespi_reseiver")
self.aws_iot_mqtt_client.configureEndpoint(kwargs['endpoint'], 8883)
self.aws_iot_mqtt_client.configureCredentials(kwargs['root_ca_path'], kwargs[
'private_key_path'], kwargs['certificate_path'])
self.aws_iot_mqtt_client.connect()
Handler method must return True on successful execution and has a list of messages in arguments. So the method just publish every message to a client generated in a constructor.
def _workout_messages(self, msgs_bunch):
""" retranslate every message to Amazon AWS IoT platform """
ret = True
for msg in msgs_bunch:
/* here we use message ident as a AWS IoT message topic and msg dict converted to json */
ret = self.aws_iot_mqtt_client.publish(msg["ident"], json.dumps(msg), 1)
if ret == False:
break
return ret
Here we are the class is ready. Include it to __init__.py to use in a project:
from .aws_iot_handler import aws_iot_handler_class
3. Specify endpoint and credentials to connect the client to AWS IoT service when calling a class constructor
# initiate the receiver
receiver = flespi_receiver.flespi_receiver()
receiver.configure(channel_id, api_key)
/* add amazon aws handler */
certdir = '/home/path/to/directory/with/certifates'
aws_handler = flespi_receiver.aws_iot_handler_class(
root_ca_path= certdir + "root-CA.crt",
private_key_path= certdir + "test_thing.private.key",
certificate_path= certdir + "test_thing.cert.pem",
endpoint = "your_service_id_string.iot.server_location.amazonaws.com"
receiver.add_handler(aws_handler)
/* start the receiver */
receiver.start()
4. Profit! See the result on AWS IoT
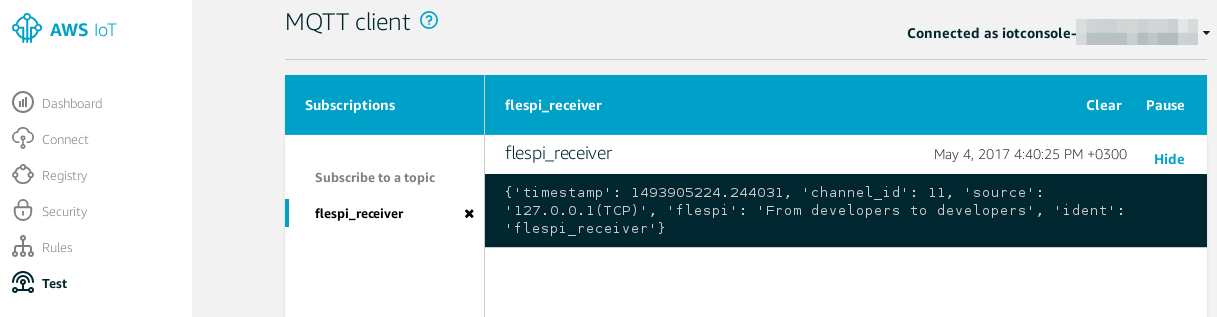
You can also create the "rule" to store incoming messages in the DynamoDB service:
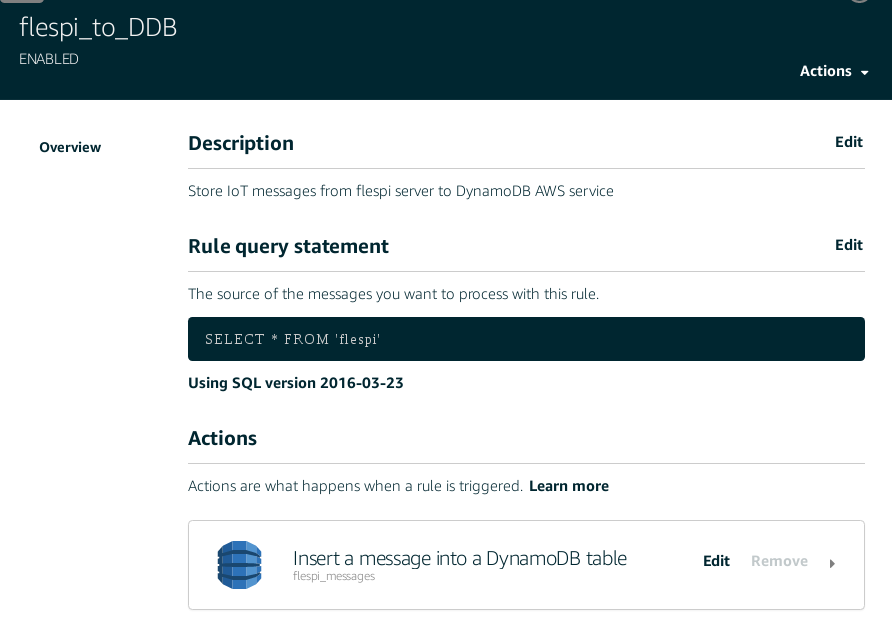
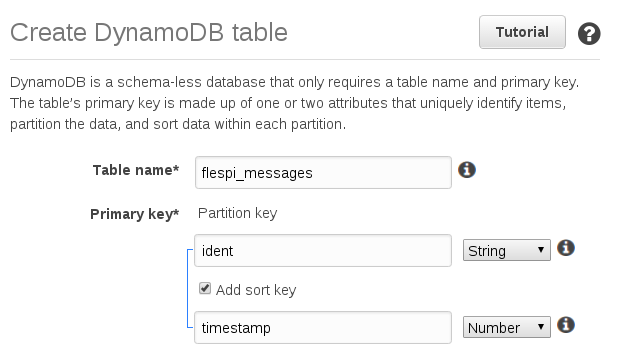
To do so you need to create a new DB: e.g. let’s take ident as a primary key and timestamp as a sort key:
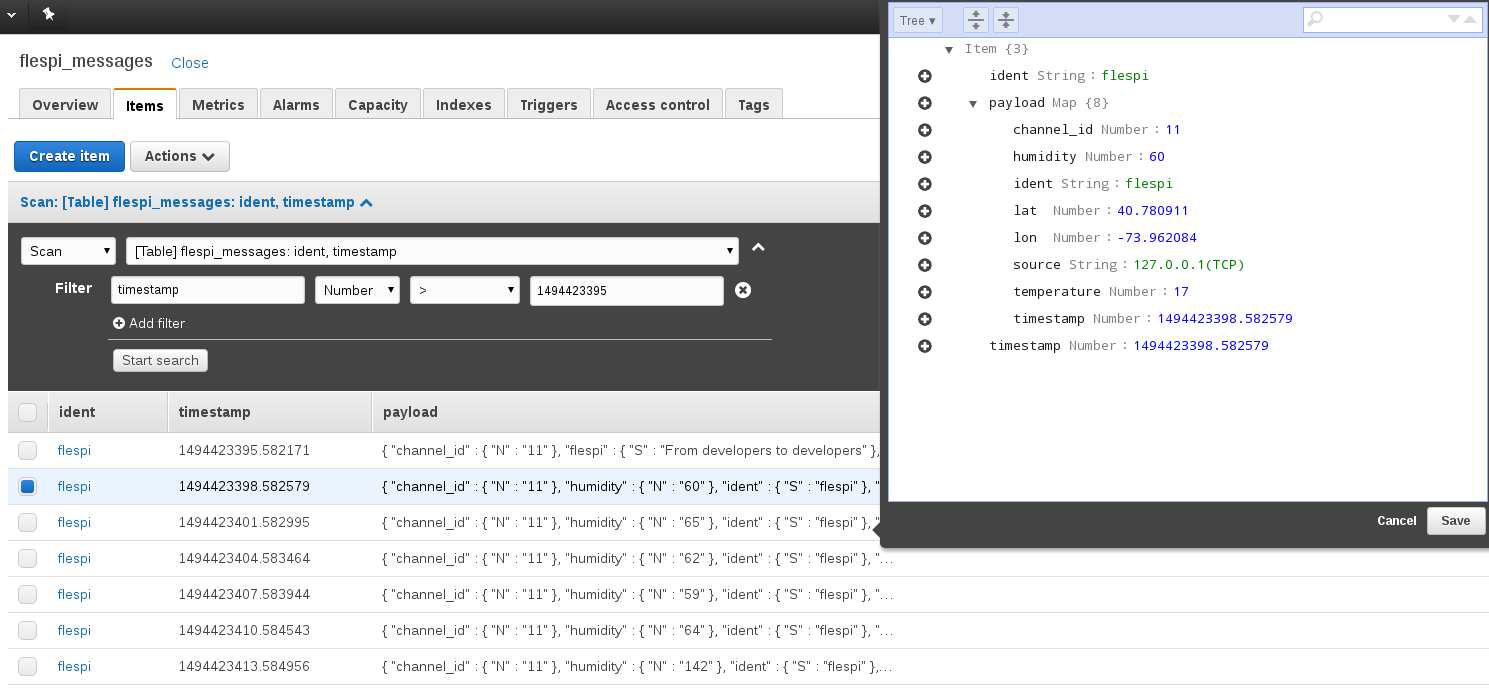
And with this settings you will receive all parameters from messages for topic "flespi" to DynamoDB table flespi_messages:
We are constantly developing our platform for the integration process to be simple, solid and flexible. All the code used in this post is available on Github. If you have any questions or suggestions please contact us in HelpBox.
