Essentials
- Streams are used to send telematics data from flespi to cloud hubs, fleet management platforms, and other services.
- Streams can forward data from specific devices, groups of devices, or entire channels.
- Only newly received messages are forwarded by the stream and in the same order as they were received by the channel or device.
- If the destination is unavailable, streams use a buffer to temporarily store the messages to be sent. Once the connection is restored all buffered messages will be flushed. Buffer stores messages for the time period specified in queue_ttl configuration field.
- Streams operate on a batch mode sending to the target each next portion of accumulated messages only once all messages from previous batch are delivered and acknowledged. The performance of stream target can be tracked with ack_latency parameter in stream log for each such batch delivery report.
- All messages sent via the stream have a record in the log. Each record has the following fields:
- ident - ident of the device whose message was sent via the stream;
- message_timestamp - timestamp of the original message sent via stream;
- device_id - id of flespi device whose message was sent via the stream (present only if the stream is assigned to Devices);
- reason - the reason why the message was skipped (the field is present if the message was not sent);
- Raw traffic between stream and its target is available for any extended diagnosis.
- When stream is disabled - it just does not work, it does not append messages to the buffer to be delivered later. Disabling the stream does not clear the messages buffer.
You can filter out messages stream is forwarding by utilizing validate_message field with expression. Only messages that satisfy the expression will be processed. For example to forward only messages with non-zero speed and coordinates present in message use next expression: "position.speed > 0 && exists('position.latitude') && exists('position.longitude')".
By using convert_message field you may replace dots in messages to different format, for example position.speed can be converted into PositionSpeed or position_speed with appropriate option selected.
Also convert_message option has fields parameter by utilizing which you may leave in the forwarded message only specified fields and remove all other. For example if you specify there ["device.id", "position.*"] messages sent by the stream will contain only device.id and position.latitude, position.longitude and position.speed parameters. This option is able to remove flespi system parameters as well.
How streams work
Streams push messages from flespi to other platforms (see how to create a stream [VIDEO]). A stream will push only newly received messages from channels or devices subscribed to the stream and in the same order as they were received. If the target platform is unavailable, the stream stores unpushed messages in its internal buffer and pushes them as soon as the target platform is up again. flespi supports several types of streams.
Note: if a stream is subscribed to a channel and a device (working over the same channel), the messages in the stream will not be duplicated and the message from the device will be forwarded.
IP whitelisting: If you protect your integration with an IP filter or firewall, please be sure to whitelist 185.213.2.10 and 185.213.2.110 IP addresses (or the whole subnet 185.213.2.0/24 that is operated solely by flespi).
Stream types
Common streams
HTTP, MQTT, Wialon Retranslator are the protocols with the open specification that can be used in your custom solution:
HTTP — sends POST requests with a list of messages to the specified URI. Max number of messages in one request can be set in the stream configuration. As soon as the server replies with 200 code, the sent messages are removed from the stream buffer.
MQTT — publishes messages to the MQTT connection (credentials specified in stream configuration). The stream uses QoS=1 to ensure that the message is removed from the stream buffer as soon as ACK from the broker is received.
AMQP - publishes messages to the AMQP Broker, such as RabbitMQ.
Pulsar - publishes messages to the Apache Pulsar messages platform.
Wialon Retranslator — sends telemetry collected from several sources (has open specification). This protocol is widely accepted by various telematics platforms.
Flespi gateway — sends data between different flespi accounts via HTTPS.
- Zoho Catalyst — full-stack cloud development platform.
Streams to cloud IoT hubs
flespi allows easily send your data to the major cloud services:
These platforms can accept the special data format implemented in flespi streams. So flespi user simply needs to configure the stream with the appropriate IoT hub credentials.
Streams to fleet management & GPS tracking platforms
Streams to specialized platforms
flespi offers ready-made solutions to push data to such platforms as:
- Thingsboard IoT platform
- Maxoptra — route optimization software
- GEFCO — logistics platform
- Redlist — maintenance platform
- e-Toll — submits telemetry to the Polish national toll road system.
- SENT-geo — the National Revenue Administration monitors road and rail transport using the SENT (System for Electronic Transport Supervision) IT system.
Media-specific streams
When device message contains media file (video, image or tacho) flespi may automatically upload such files to alternative storage system via specialized streams:
How to create a stream?
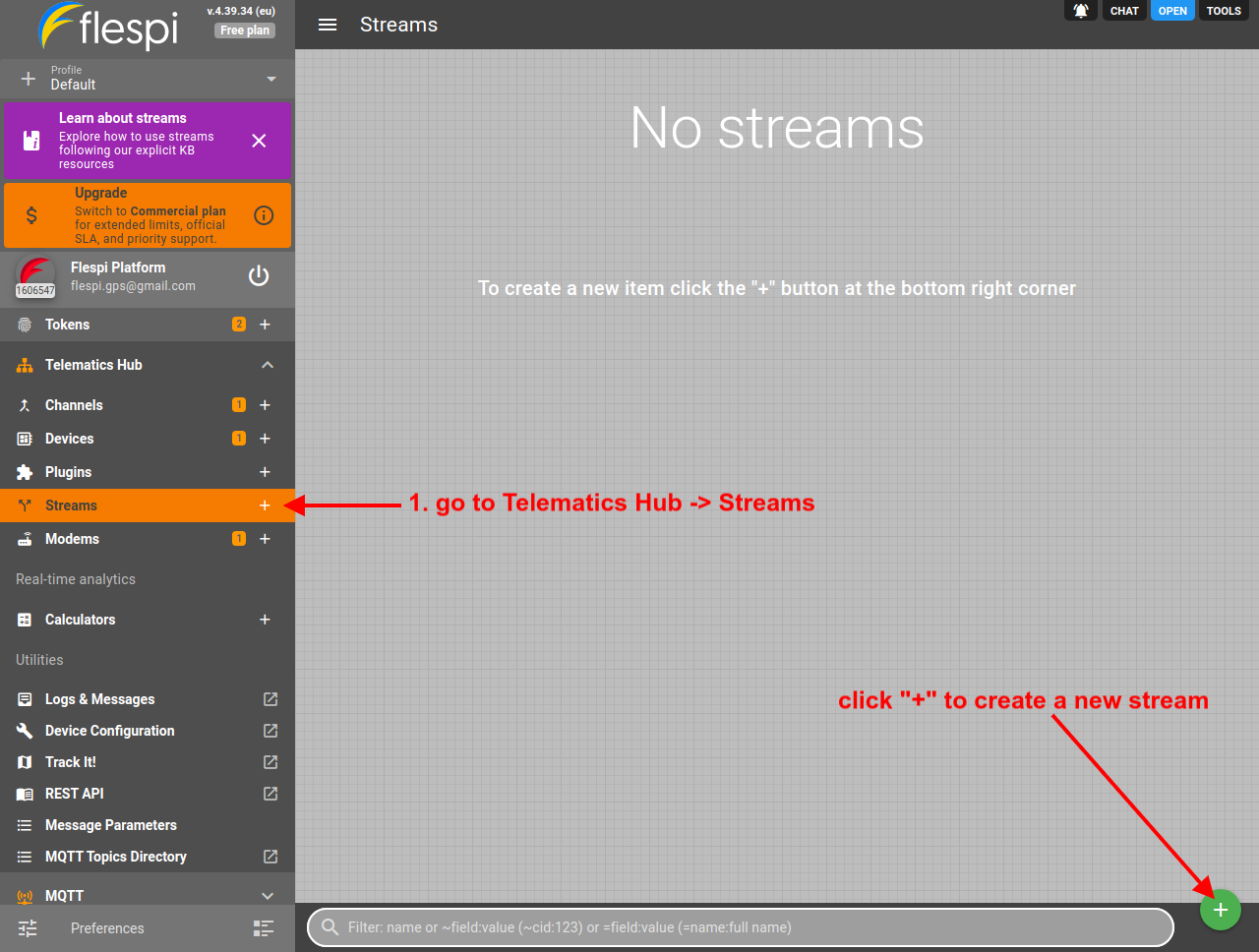
- Log in to the flespi panel
- Navigate to Telematics hub -> Streams and click the "+" button in the bottom right corner to add a new stream:
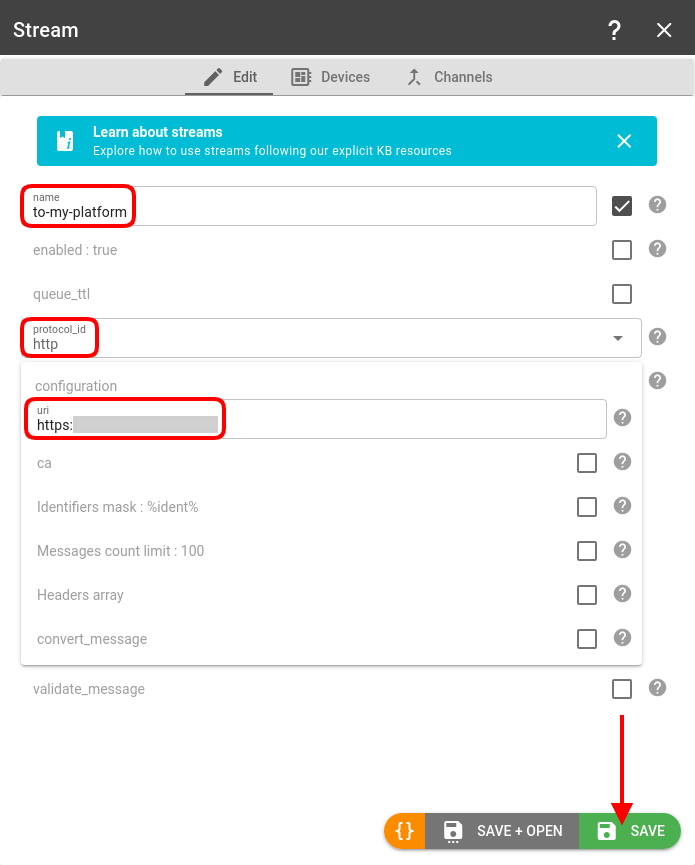
- Give the new stream a name, pick the proper stream type depending on the destination platform, configure it, and click Save:
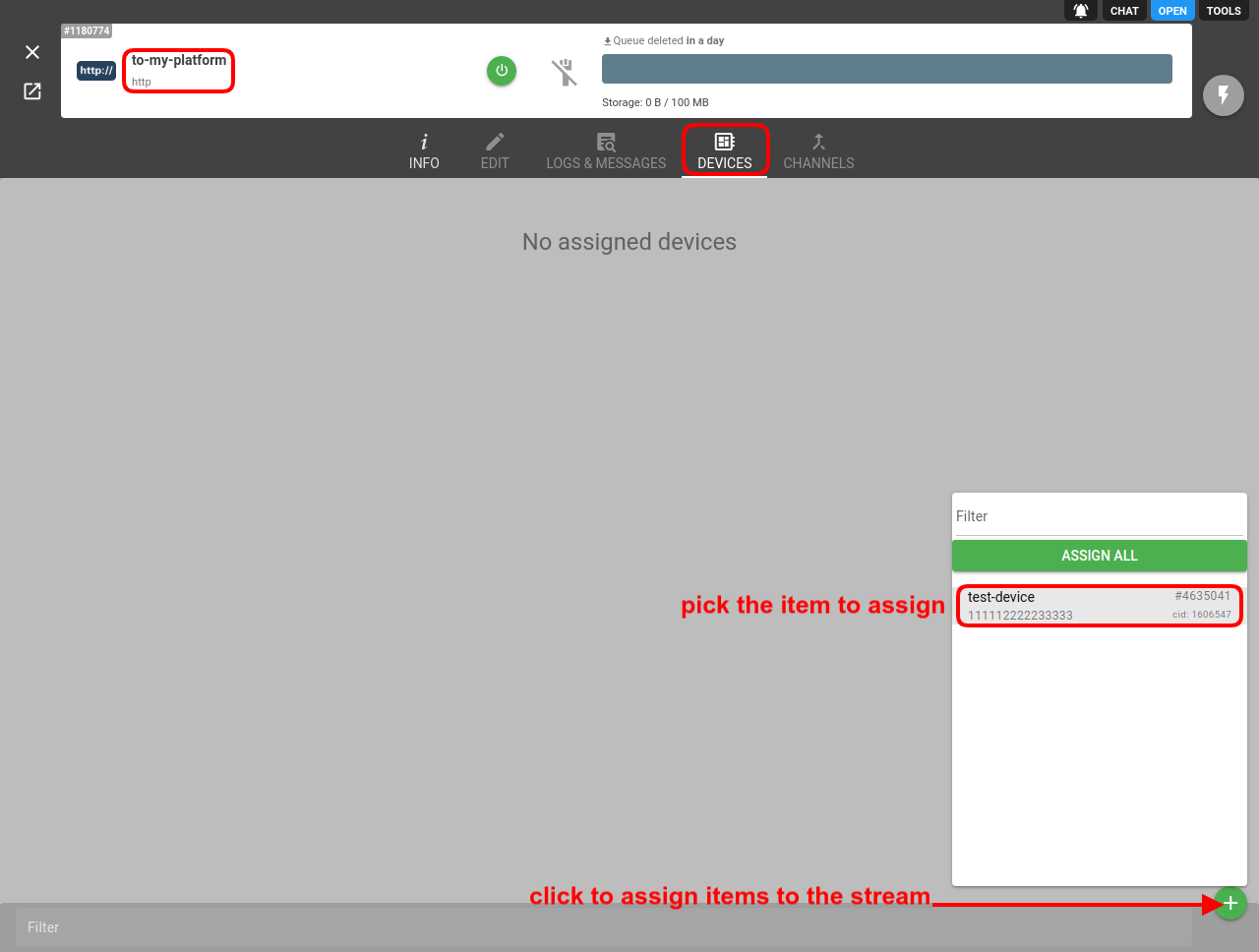
- For the stream to start sending messages it has to be subscribed to device(s) or channel(s). Go to the respective tab on the stream card and assign desired items to the stream:
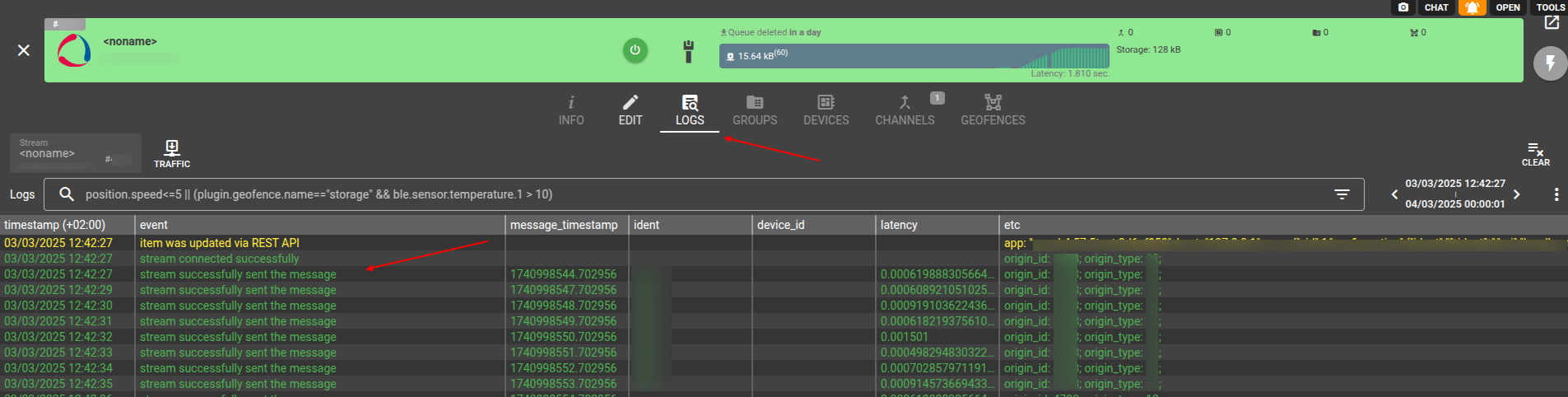
- Once the assigned device starts sending messages, the stream with start forwarding them to the target platform. You can check the Logs & Messages for the stream to see the "stream successfully sent the message" records:
Streams API
To perform any operations with the streams, use the streams API.
You can monitor stream messages forwarding status via following MQTT topics:
- flespi/log/gw/streams/{stream_id}/connecting - stream started initiating connection to the target (event_code=407, reported only for certain stream types);
- flespi/log/gw/streams/{stream_id}/connected - stream successfully connected to the target (event_code=401, reported only for certain stream types);
- flespi/log/gw/streams/{stream_id}/closed - stream closed connection to the target (event_code=402, reported only for certain stream types);
- flespi/log/gw/streams/{stream_id}/failed - stream failed to establish connection to the target, failed to deliver single message or messages batch to the target (event_code=403 for failed connection or messages batch and event_code=406 for individual message that was skipped);
- flespi/log/gw/streams/{stream_id}/succeeded - stream successfully delivered message to the target (event_code=405);
Troubleshooting
In case of any issues, check the Logs tab on the stream screen:
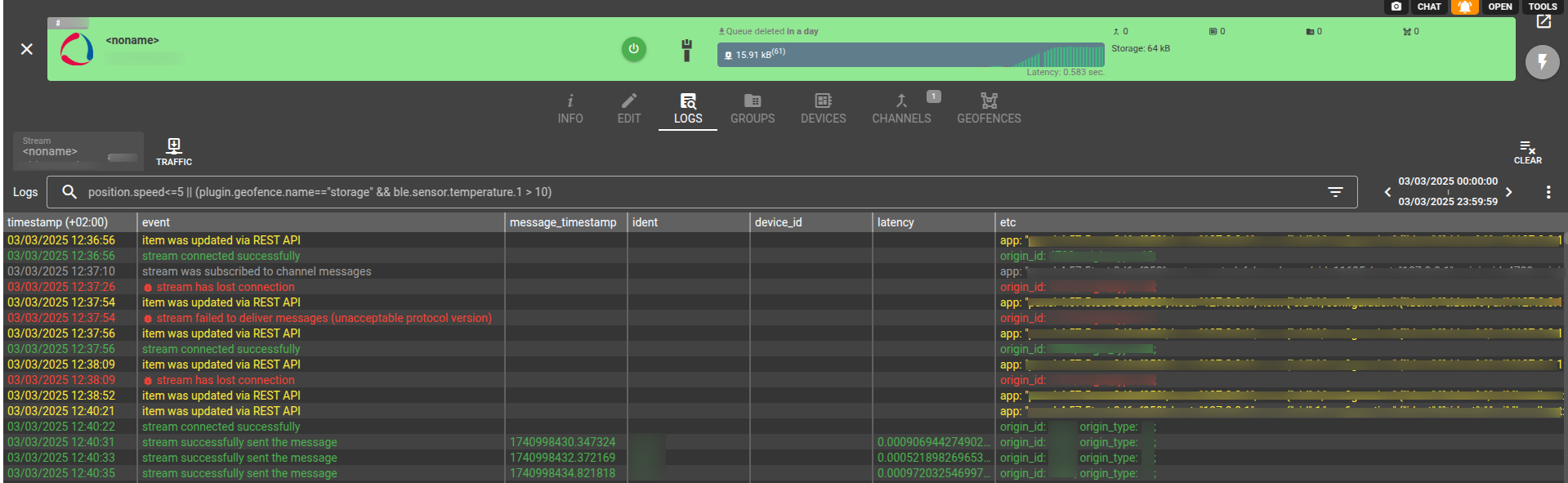
Log entries show which messages were sent and which were skipped. The reason field of the log message tells you why the message was skipped. The ack_latency parameter shows how long it took to send a batch of messages. You can use device_id, ident and message_timestamp parameters to identify which message from which device (or channel) this stream log record corresponds to.
You can also view stream traffic — full data exchange between flespi and the 3rd party platform:
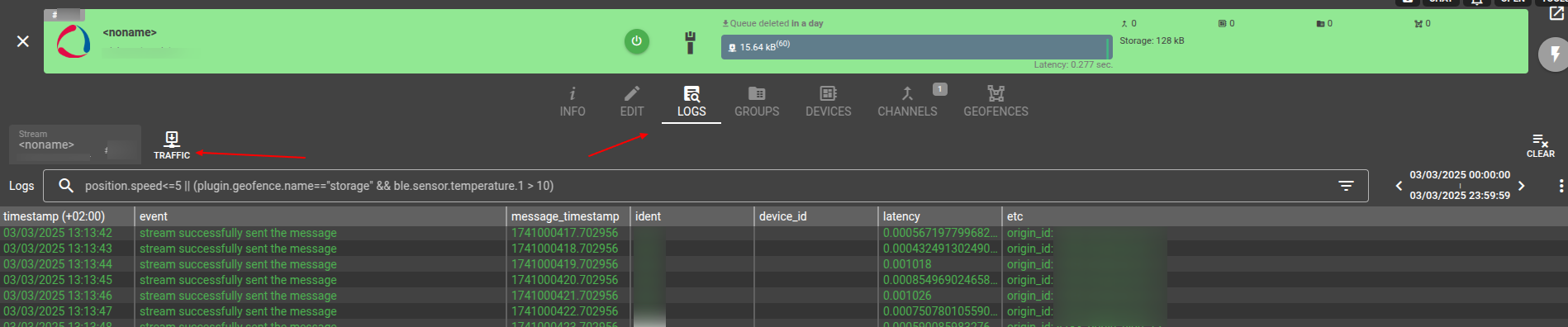
You can quickly navigate to a raw traffic associated with certain log event by right clicking on a log message and selecting "Show Traffic" in the context menu. This action will switch the view to a traffic view and navigate to the corresponding traffic generated by the stream and related to this event in stream logs.